Results from the Nationwide Administrative Database in Japan concerning adults diagnosed with septic shock and requiring noradrenaline support during the period 2016-2019 have been published in the Blood Purification journal by Fujimori and co-workers.
The article is available here.
Results on a population of 4,141 patients per group showed:
a statistically significant 28 day-survival improvement in patients treated with Polymyxin B hemoperfusion therapy (PMX-HP) compared to the control group (77.9% in the PMX-HP group and 71.1% in the control group ,p < 0.0001).
In addition, PMX-HP significantly reduced the number of days on noradrenaline, continuous hemodiafiltarion (CHDF) and mechanical-ventilation.
No questioning concerning PMX-HP safety was raised.
This study represents a further step in the clinical evidence of PMX-HP in the management of septic shock patients and thus contributes to the clinical research progress on the role of Blood Purification therapies in sepsis and septic shock.
Methods
The authors conducted an observational propensity-matched analysis on adult patients hospitalized in Japanese ICUs during the period 2016-2019, diagnosed with septic shock requiring noradrenaline support. Propensity-score matching was used to compare the outcome of patients between PMX-HP-treated and non-treated patients.
Endpoints
The primary endpoint was 28-day survival improvement counting from the day of noradrenaline initiation.
Secondary endpoints were noradrenaline-, ventilator- and CHDF-free days at day 28.
Results
- Of 30,731 eligible patients, 4,766 received PMX-HP.
- Propensity-score matching produced a matched cohort of 4,141 pairs.
- The 28-day survival rate was 77.9% in the PMX-HP group and 71.1% in the control group (p < 0.0001).
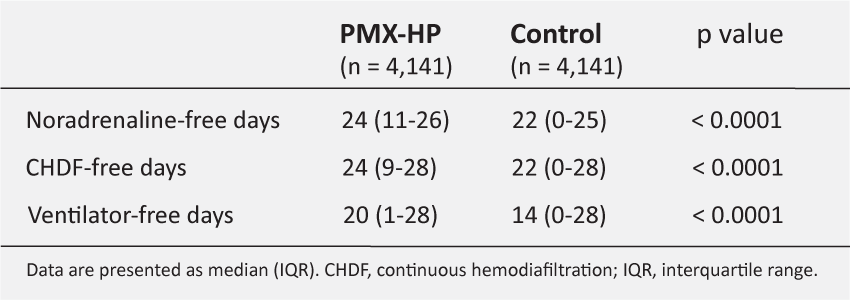
- Noradrenaline-free days at day 28 was 24 (11-26) days in the PMX-HP group vs. 22 (0-25) days in the control group (p < 0.0001).
- CHDF-free days at day 28 was 24 (9-28) days in the PMX-HP group vs. 22 (0-28) days in the control group (p < 0.0001).
- Ventilator-free days at day 28 was 20 (1-28) in the PMX-HP group vs. 14 (0-28) in the control group (p < 0.0001).
Conclusioni
To date, this is the biggest published analysis of a nationwide database and one of the largest data-analyses on septic shock patients available in literature.
The study shows that PMX-HP treatment might be useful in reducing the mortality of septic shock patients requiring noradrenaline.
PMX-HP also significantly reduced the number of days of noradrenaline, CHDF, and mechanical-ventilation requirement.
No questioning concerning PMX-HP safety was raised.
This study represents a further step in the clinical evidence of PMX-HP for the management of septic shock patients and thus contributes to the clinical research progress on the role of Blood Purification therapies in sepsis and septic shock.
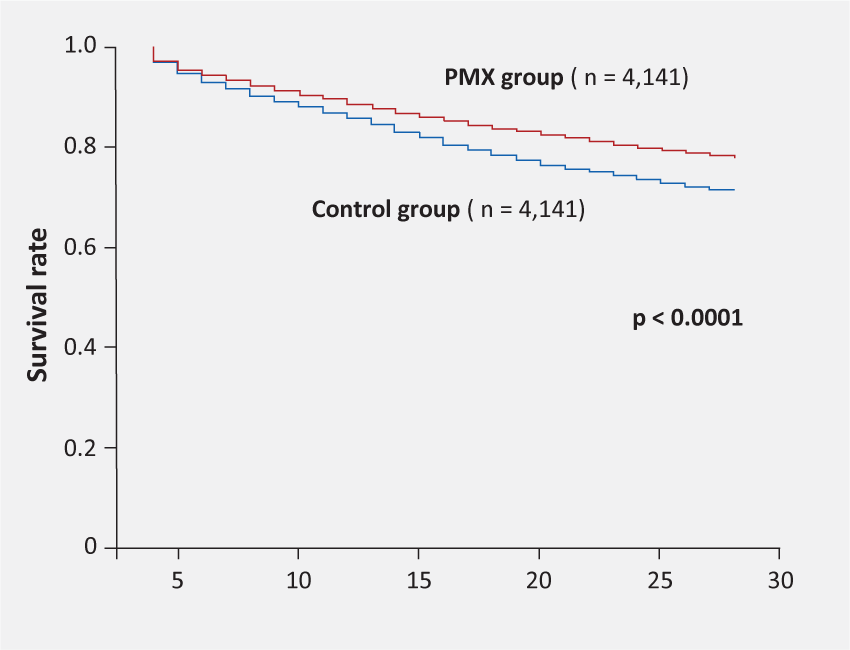
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier survival curves of propensity-matched patients.
Table 1. Noradrenaline-, ventialtor- and CHDF-free days at day 28.
The article is available here.